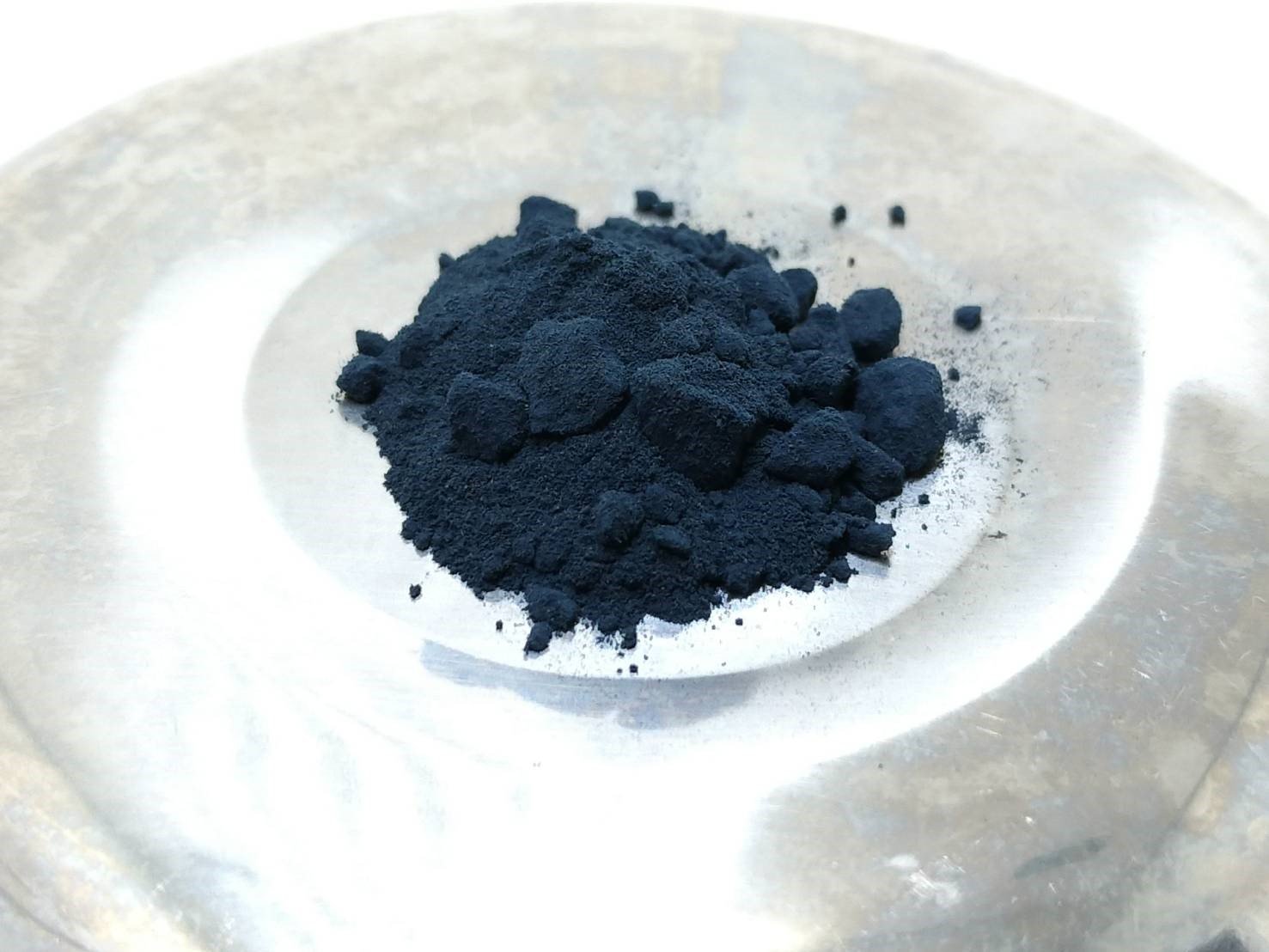
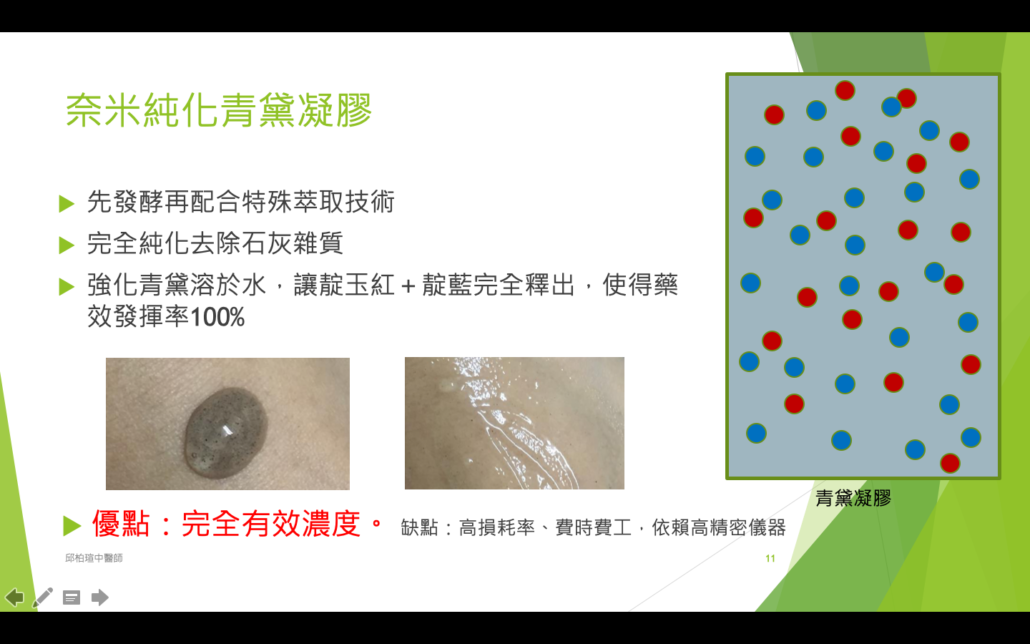
青黛
由爵床科植物馬藍Strobilanthes cusia(Nees) Bremek.、蓼科植物蓼藍PolygonumtinctoriumAit.十字花科植物菘藍IsatisindigoticaFort.豆科植物木藍IndigoferatinctoriaL.四種植物的莖葉經加工製得的乾燥粉末或團塊。
製藥過程
1.日出前將植物採收
2.將枝葉浸泡入特定氣候環境土質的水坑中
3.利用該環境有特定菌種,發酵三天
4.取出枝葉,並加入石灰
5.攪拌直到出現靛青色泡沫
6.收集水坑中的沈澱物
7.烘乾沈澱物,就是市面上所見的青黛
青黛成分
1.植物枝葉碎渣 2.塵土 3.石灰 4.乙醇
主要有效成分
靛玉紅(indirubin):含量不低於0.3%
靛藍(indigo ):含量不低於2%
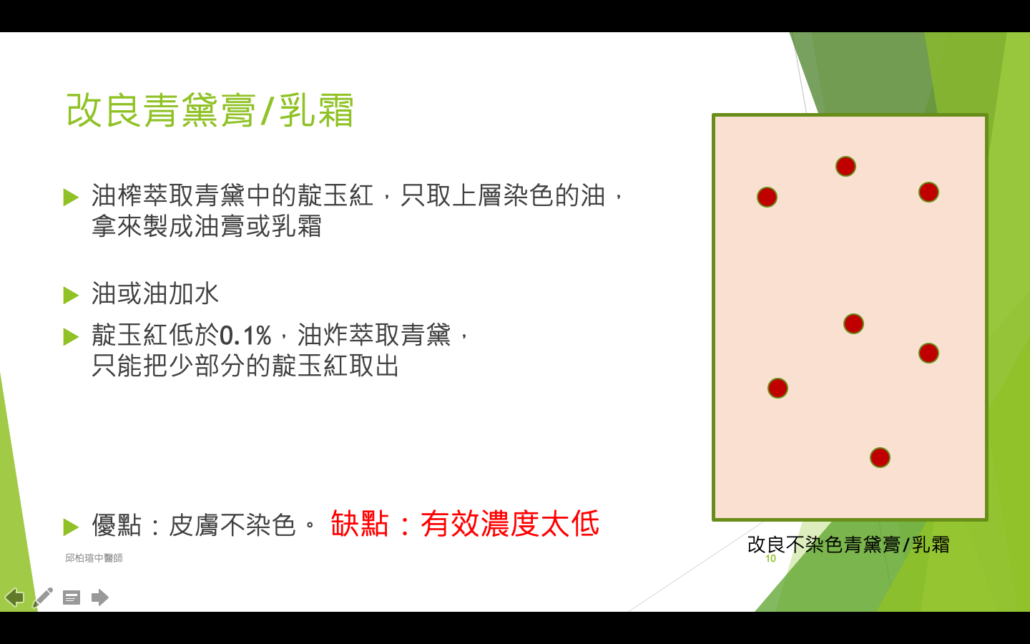
青黛外用製劑

青黛(せいたい)
青黛(せいたい)は、ヨウジャク科のマラン、センノウ科のセンラン、アカバナ科のソウラン、マメ科のモクランの4種類の植物の茎と葉を加工して得られる乾燥粉末または塊です。
製薬過程
- 日の出前に植物を収穫します。
- 茎葉を特定の気候と土壌環境の水たまりに浸します。
- その環境に特定の細菌種が存在するため、3日間発酵させます。
- 茎葉を取り出し、石灰を加えます。
- 青紫色の泡が現れるまでかき混ぜます。
- 水たまりから沈殿物を収集します。
- 沈殿物を乾燥させると、市販の青黛になります。
青黛の成分
- 植物の茎葉の破片 2. 土壌 3. 石灰 4. エタノール
主要な有効成分
インディルビン(indirubin):含有量は0.3%未満であること。
インディゴ(indigo):含有量は2%未満であること。
Qing Dai
Qing Dai, also known as indigo naturalis, is a dried powder or clump obtained from the stems and leaves of four types of plants: Strobilanthes cusia (Nees) Bremek. from the Acanthaceae family, Polygonum tinctorium Ait. from the Polygonaceae family, Isatis indigotica Fort. from the Brassicaceae family, and Indigofera tinctoria L. from the Fabaceae family.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Process
- Harvest the plants before sunrise.
- Soak the stems and leaves in water pits with specific climatic and soil conditions.
- Utilize specific strains of bacteria present in the environment for fermentation over three days.
- Remove the stems and leaves, and add lime.
- Stir until an indigo-colored foam appears.
- Collect the sediment from the water pits.
- Dry the sediment, resulting in the Qing Dai powder commonly seen in the market.
Composition of Qing Dai
-
- Plant stem and leaf fragments
- Soil
- Lime
- Ethanol
Key Active Ingredients
Indirubin: Content not less than 0.3% Indigo: Content not less than 2%